Sexual Revolution at UNC

This collection follows transformations among UNC-Chapel Hill LGBTQIA+ students at the intersection of gender, race, and class during and the sexual revolution of the 1960s and 1970s, tracing its impact on their lives, relationships, and activism during those decades and later years.
UNC Foodworkers' Strikes

This collection focuses on the 1969 food worker strikes at UNC-Chapel Hill against the UNC Food Service and SAGA Food Service. Interviewees include campus food workers, mostly African American women; students; strike mediators; lawyers; faculty; and university officials. The interviews speak to the larger political context of the strike and its connection to social movements calling for change at the nexus of racial, class, and gender-based injustice.
Pearsall Project

This collection includes interviews with key players behind the Pearsall Plan for school desegregation in North Carolina. Proposed in 1956 by Rocky Mount, N.C., attorney Thomas Jenkins Pearsall, the plan gave local school boards the power to close schools rather than desegregate. It placed the burden of desegregation on individual African Americans rather than the state and invited public blame of Black students and families as "troublemakers."
North Carolina Community Colleges Presidents of Color

This collection highlights the personal and career stories of Black, Latinx, Asian and Indigenous leaders in the North Carolina Community College System as part of the Trailblazer Profiles project, a collaboration between the SOHP and the Belk Center for Community College Leadership and Research at NC State University. The profiles aim to elevate and center the work of community college leaders of color in North Carolina and inspire support for diversifying the presidential leadership pipeline.
Chapel Hill's Lincoln High School

This collection includes interviews with former teachers, staff, and students from Chapel Hill, N.C.'s Lincoln High School, the historically black secondary school that closed in 1962 when a school desegregation plan was implemented. Interviewees discuss African American life and race relations in Chapel Hill, as well as education, discipline, extracurricular activities, and high school social life before and after integration.
Racial justice at UNC
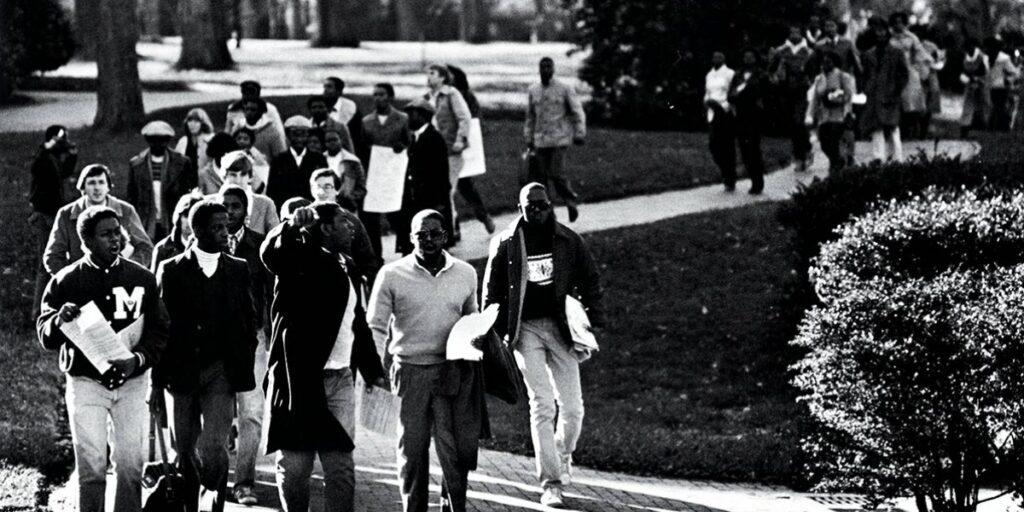
This collection features stories from students, staff, and faculty at UNC-Chapel Hill working to achieve racial justice on campus from the 1960s through the 2010s. It highlights intersectional Black-led organizing, from the Black Student Movement founded in 1967 to the Real Silent Sam Coalition founded in 2011.
Black Pioneers

This collection highlights the stories and challenges of the first Black students to attend UNC-Chapel Hill.
Piedmont Industrialization

This collection includes interviews from workers in tobacco, textile, and hosiery industries in the NC Piedmont during the first half of the twentieth century. Some interviewees also discuss farming, saw milling, or domestic service jobs. Interviews focus on work conditions, the division of labor by gender and by race, labor policies, labor unions, and strikes. Other topics include racism, family life, living conditions, education, recreation, and health.